ᐈ Суши Сеты Доставка По Городу Киев Заказать Вкусные Суши Сеты На Дом Или Офис В Киеве
EUPs deliver clarity and precision to the messy world of multi-stage manufacturing, optimizing prices, stock, and manufacturing. In a process costing system, the value of units transferred out of each division have to be determined in addition to the value of any partially completed items remaining within the division. Based Mostly on the earlier calculations, the next seven value results could be determined.
Step 1: Equal Units Of Starting Wip
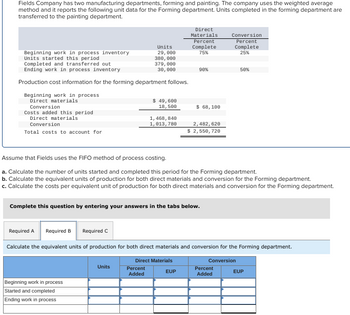
Accountants name the combined labor and overhead prices conversion costs. Conversion prices are these costs incurred to transform raw supplies into the ultimate product (meaning, direct labor and overhead). Once the equivalent items for materials and conversion are known, the cost per equivalent unit is computed in a similar method because the items accounted for. The prices for materials and conversion need to reconcile with the entire starting stock and the prices incurred for the department throughout that month. As described previously, process costing can have a couple of work in course of https://www.personal-accounting.org/ account.
- This implies that the company began producing a hundred and five bicycles in the course of the interval.
- (b) completed from beginning inventory, items began and completed during the period, and units partially completed in ending inventory.
- In FIFO, each starting and ending inventories are primarily converted to an equivalent items basis.
- The FIFO methodology makes use of these equivalent units by assigning the oldest costs to the items accomplished first, which helps observe costs within the order they were incurred.
2 Equivalent Models (weighted Average)
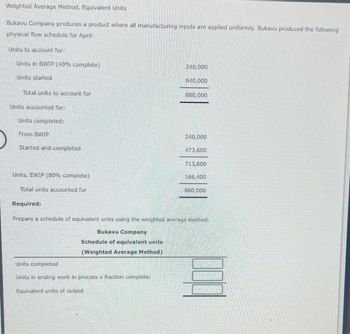
For instance, if we deliver 1,000 items to a 40 % state of completion, that is equivalent to four hundred models (1,000 x 40%) which are 100 percent full. Accountants base this idea on the supposition that an organization must incur roughly the same amount of costs to deliver 1,000 units to a 40% degree of completion as it will to finish four hundred items. Calculating the began quantity is a elementary step in understanding the production process and managing inventory effectively. The beginning work-in-process was valued at $66,000, consisting $20,000 of transferred-in prices, $30,000 of material prices, and $16,000 of conversion prices.
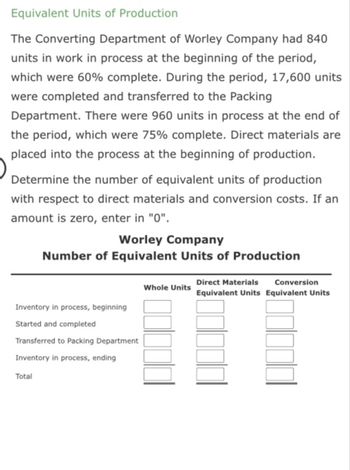
Now you can determine the value of the units transferred out and the cost of the items still in process within the shaping department. The beginning step in computing Department B’s equal items for Jax Company is determining the stage of completion of the two,000 unfinished models (remember units completed and transferred are all the time 100% complete). In Division B, the ending items may be in different stages of completion concerning the supplies, labor, and overhead costs. Assume that Division B adds all materials firstly of the production process. Then ending inventory can be one hundred pc full as to materials since we obtained all materials firstly of the process. Units accomplished and transferred are finished items and can all the time be 100% full for equal unit calculations for direct supplies, direct labor and overhead.
For these items that have been in the beginning inventory, we have to figure out how much work was DONE on them on this period to get them to the purpose of being transferred to the next process. For those items in the ending stock, it’s the similar because the weighted-average method, the place we have to calculate how much work has been done to them already. At the top of process 1, our planners have their paper and ink ready to be printed. Let’s assume we determine the ending WIP inventory to be 35% complete as to the process. If we now have 1000 units in the ending WIP stock after course of 1, this would equal 350, using the formula for equal models. We could then add these equal models to the ending WIP stock for process 1.
What Do You Imply By Accomplished During The Period?
Underneath the weighted common methodology, we use beginning work in process prices AND prices added this era. Under you’ll discover an example of a mini-lesson that helped my scholar, Wanda, perceive how to calculate the began and completed items. The materials prices consisted of $30,000 in beginning inventory and $88,000 incurred in the course of the month, for a complete of $118,000. (3) Group three has 7,300 (given) models started this month to be accomplished next month.
Any units that have been moved into process 2, will be subtracted from the WIP stock for process 1. Work in process inventory is an asset The ending work in process stock is simply the value of partially completed work as of the tip of the accounting period. Ending WIP is listed on the company’s stability sheet together with amounts for raw supplies and finished items. The take-away here is that either method will end up with the identical prices being moved forward with the completed items to the next course of. These prices will be added to additional costs as the product strikes via each of the processes until it arrives in the completed items stock.
The equal units of production underneath the FIFO technique include work done in the current period only. So from our instance above, we now have 4925 equivalent units of manufacturing using the weighted common methodology. If our complete price of our beginning WIP stock was $1,000 and we added $10,000 through the interval. Equal items of manufacturing is a crucial idea how to calculate the started and completed units in value accounting, especially for companies that manufacture merchandise by way of multiple processes. It allows producers to accurately observe production output and allocate prices even when some units usually are not but complete. In this comprehensive information I’ll clarify what equal units of production are why they matter, and stroll by way of the step-by-step course of for calculating them.
This represents the variety of models that were already in the production process firstly of the accounting interval. These items are partially accomplished and will proceed to be labored on through the interval. 4800 models × $2.09 plus the $658 of prices incurred for the start stock that was transferred out.
In addition to the equal units, it’s necessary to trace the units accomplished in addition to the items remaining in ending inventory. A related course of is used to account for the prices completed and transferred. Reconciling the number of items and the prices is part of the process costing system. The reconciliation includes the whole of beginning stock and units began into production.